Transgenic and Genome Editing Facility
The Transgenic and Genome Editing Facility (TGEF) serves primarily the Brown University community, including its affiliated research institutes and hospitals, at a base fee-for-service. We are also open to other institutes with rates higher than the base cost.
Transgenic and Genome Editing Facility
The Transgenic and Genome Editing Facility (TGEF) serves primarily the Brown University community, including its affiliated research institutes and hospitals, at a base fee-for-service. We are also open to other institutes with rates higher than the base cost.
Address/Contact
Transgenic and Genome Editing Facility, Brown University
70 Ship Street, Room 205
Providence, Rhode Island, 02903
Phone: (401) 863-9544
Team
-

Jinping Luo
Dr. Luo supervises the overall operation of the facility and provides consultation to investigators.
-

Zuping Qu
-

Johannes Fimmers
Research Assisant, Transgenic Facility, BioMed/MCB department
Service Request and Reservations
Please go to Brown University iLab
Login with your Brown credentials and select the Transgenics and Genome Editing Core from the drop-down menu. Then click on “request services” and follow the instructions for reservations and billing.
New External and Commercial customers click here
For further information or if you require services that are not listed here, please contact Jinping Luo, the facility director.
Rates
FY26 Rates
Service | Units | Internal Academic Rates* | External Academic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genotyping | |||
| Gel determination | Sample | $3 | $5 |
| Long-Read Sequencing | Sample | $17 | $27 |
| Sanger Sequencing | Sample | $8 | $13 |
| CRISPR | |||
| Guide RNA Validation plus Cas protein | Target Site | $607 | $968 |
| Donor_Long Single-Strand DNA (LssDNA) | Project | $1,069 | $1,705 |
| Donor_Single-Strand Oligodeoxynucleotide (ssODN) | Project | $169 | $269 |
| Donor_Plasmid Construction | Project | $1,839 | $2,932 |
| Embryo Microinjection/Electroporation | |||
| Mouse Embryo MJ/EP (B6, FVB, or CD-1) | Project | $4,120 | $6,571 |
| Rat Embryo MJ/EP (SD) | Project | $6,213 | $9,910 |
| Germline Transmission | |||
| Mouse Germline Transmission (mGLT) | Project | $1,020 | $1,626 |
| Rat Germline Transmission (rGLT) | Project | $2,019 | $3,221 |
| Cryopreservation | |||
| Embryo Cryopreservation (Homozygotes or Heterozygotes) | Line | $924 | $1,474 |
| Sperm Cryopreservation | Line | $439 | $700 |
| Mouse line Cryo Recovery | |||
| Mouse Line Recovery from Frozen Embryos | Line | $1,149 | $1,832 |
| Mouse Line Recovery from Frozen Sperm | Line | $1,349 | $2,151 |
| In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) | |||
| Mouse Colony Scale-Up | Line | $2,092 | $3,337 |
| Mouse SPF Rederivation | Line | $1,649 | $2,629 |
| Individual Services | |||
| Annual Cryo Storage Fee | Year | $107 | $171 |
| Hourly Rate for custom projects not listed | Hour | $69 | $109 |
*Rates for Brown and Rhode Island Academic and Hospital Affiliates. For External Academic or Commercial Rates, contact Jinping Luo.
Rates Effective 11/5/2025
Services and Instruments
Flow Charts & Timelines
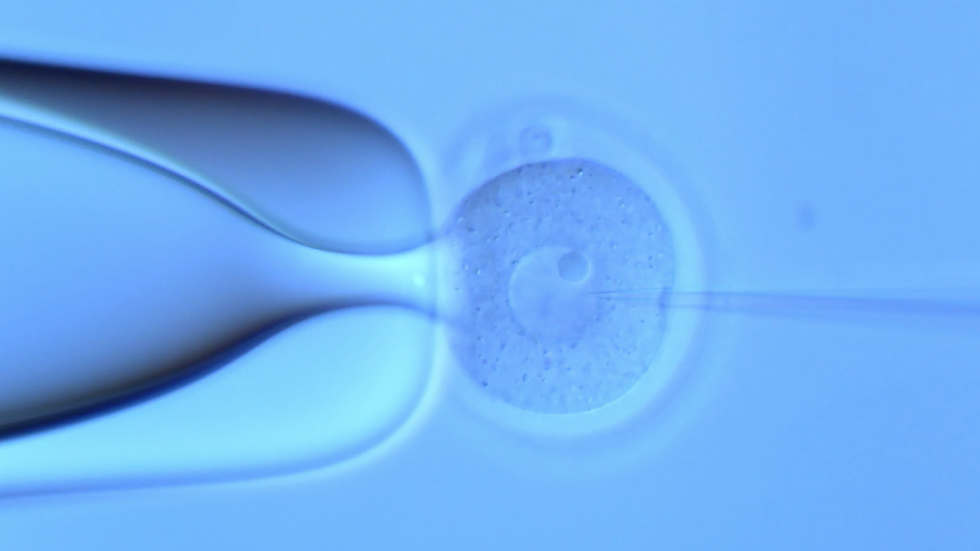
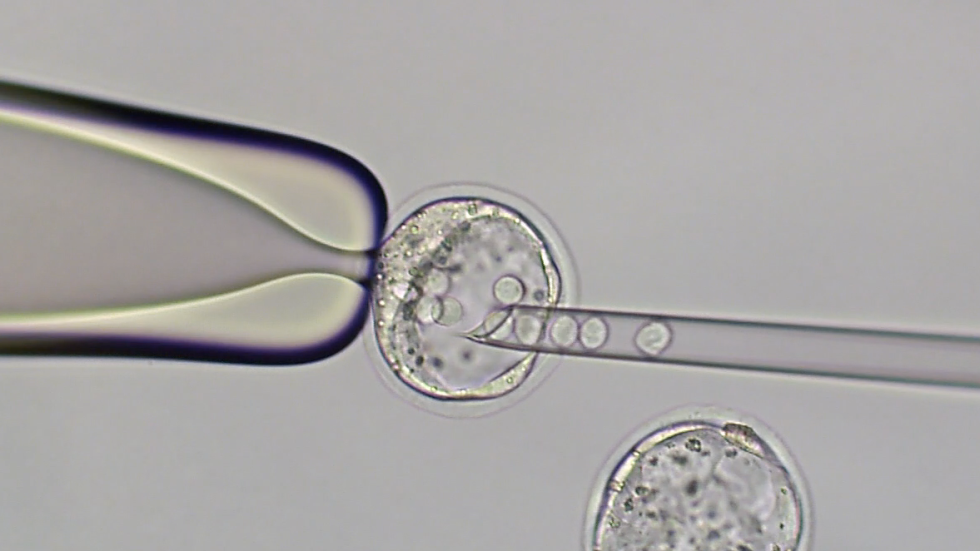
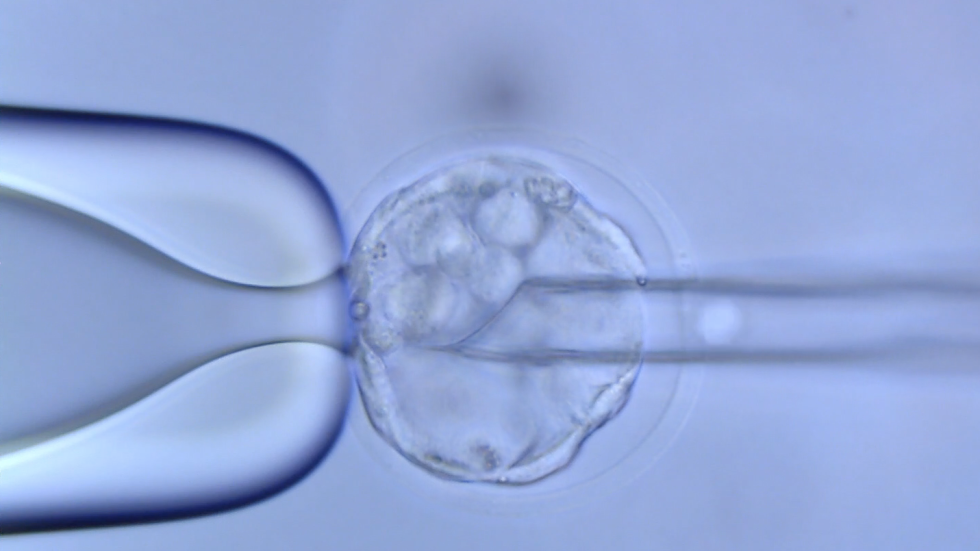
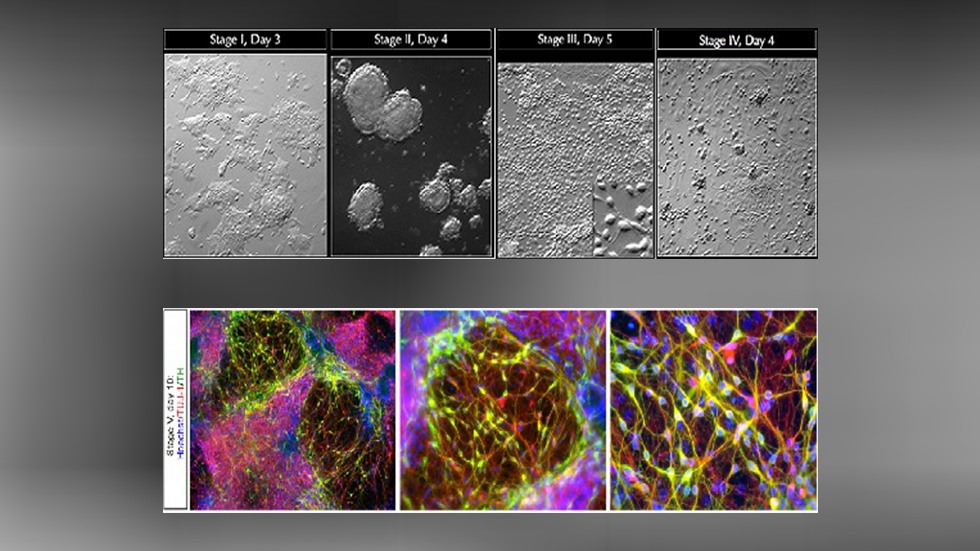



Resources for Grants
Acknowledgment
This facility was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Brown University's Division of Biology and Medicine and Provost's office.
The following acknowledgement must appear in any publication made possible by the work of the Transgenic Facility.
"This project was supported by the Mouse Transgenic and Gene Targeting Facility at the Brown University that was funded by a grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (P30 GM103410) from the National Institutes of Health."
Links to Resources
External Resources
CRISPR Design Tools
one should choose target sites with high out-of-frame scores.
ES Cells
The following are sources for constructs, Genetrap ES cells, and WT ES cells. If you are considering using cells from these sources for microinjection at Brown, please contact the facility prior to purchase.
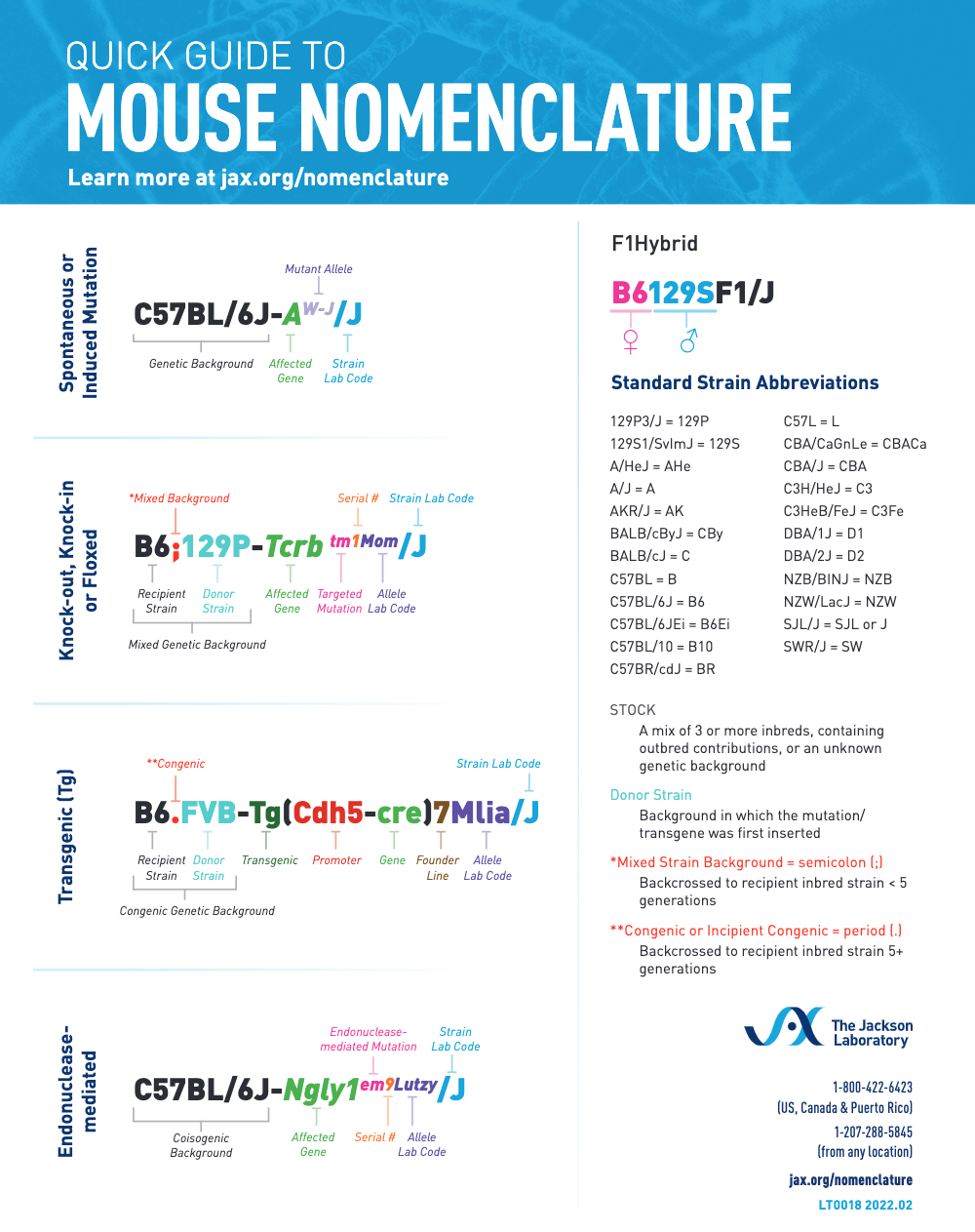
Mouse Model Nomenclature
Montoliu Lluís & Whitelaw C. Bruce A. (2010) Using standard nomenclature to adequately name transgenes, knockout gene alleles and any mutation associated to a genetically modified mouse strain. Transgenic Research (ePub, 16 July 2010)
"The International Society for Transgenic Technologies (ISTT) and the scientific journal, Transgenic Research, to which the ISTT is associated, have decided to promote the use of standard nomenclature for naming mouse strains, genes, mutations and alleles. In this regard, and according to ISTT aims and activities, ISTT will disseminate in its web site, blog, newsletter and Transgenic Technology (TT) meetings, information and recommendations to use standard nomenclature. Likewise, the correct use of rules and guidelines for standard nomenclature for naming mouse strains, genes, mutations and alleles will be enforced in subsequent articles submitted to Transgenic Research for publication, as it is already done in several other journals."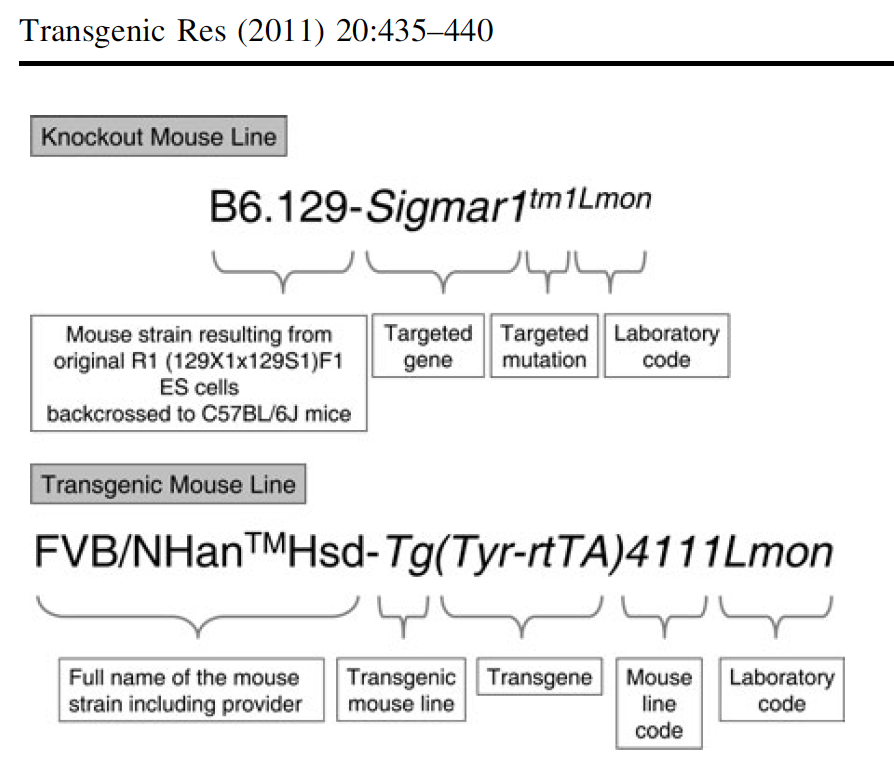
https://www.jax.org/jax-mice-and-services/customer-support/technical-support/genetics-and-nomenclature