Proteomics Facility
The Proteomics Core provides protein and proteomic analysis instrumentation for protein identification, characterization, and quantification.
Proteomics Facility
The Proteomics Core provides protein and proteomic analysis instrumentation for protein identification, characterization, and quantification.
About
The Proteomics Core Facility's mission is to provide well-maintained, state-of-the-art instrumentation and fundamental proteomics expertise to Brown University and the Rhode Island scientific community. We aim to be a focal point of intellectual activity in proteomics by enabling nationally recognized proteomics research within Rhode Island. The Proteomics Core Facility provides training in emerging proteomic techniques and has a strong commitment to be at the leading edge of current and developing technologies and provide consultation on their application. We welcome inquiries from scientists and teachers seeking information regarding how we may assist them in furthering their research and educational goals.
Find us at CoresRI!
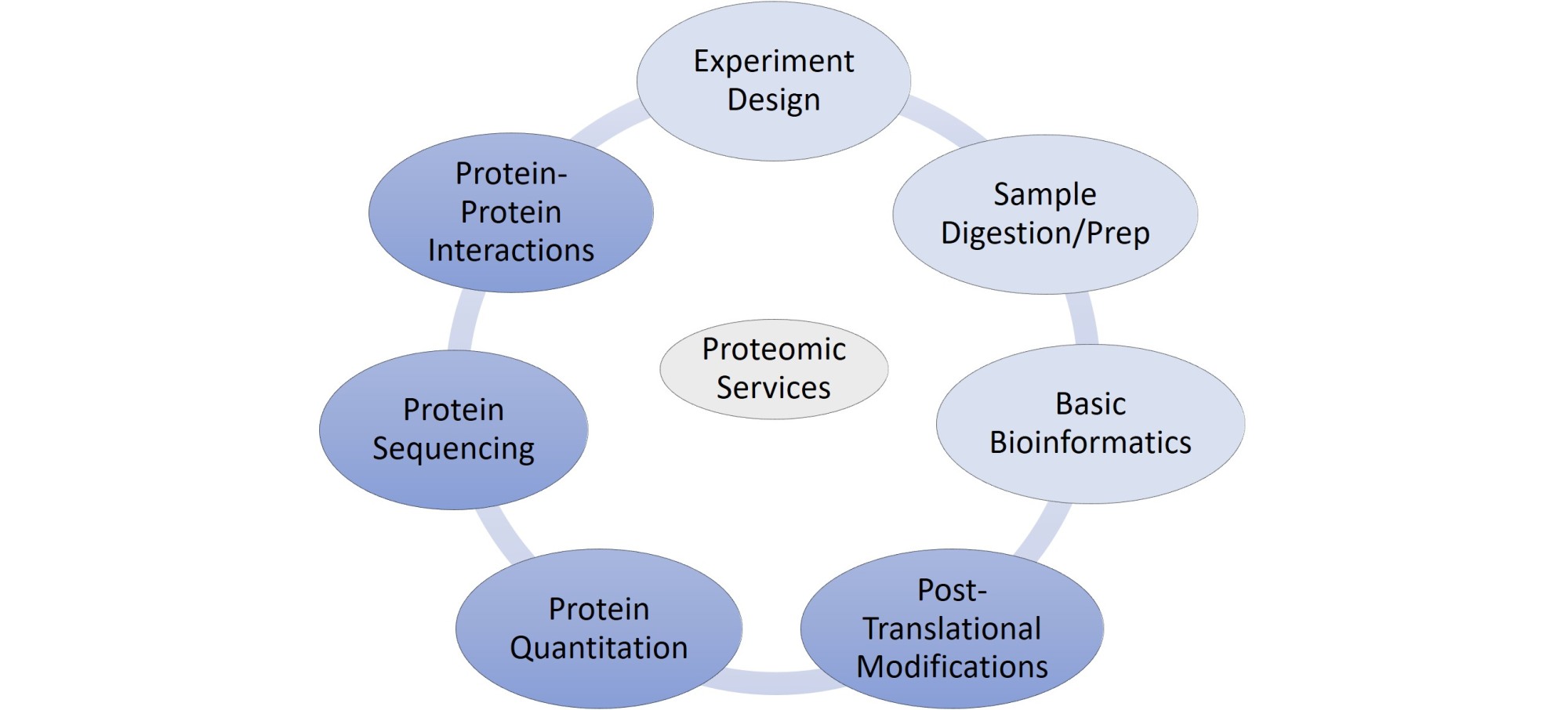
Services and Instruments
Description of Services
Basic
♦ Includes S-Trap protein digestion, desalting, and LC/MS analysis. Thermo .raw files are the
only deliverable.
Complete – Protein Profiling
♦ Includes what is offered in Basic Service with the deliverable being an Excel report of
Protein IDs and % Abundance from Spectromine/Spectronaut/Proteome
Discoverer/MaxQuant where appropriate. All users select this option for protein profiling,
unenriched PTM analysis, and label-free quantitation projects.
Complete – Co-IP Interactomics
♦ Includes what is offered in Basic Service with additional sample cleanup, an Excel
report of Protein IDs, and % Abundance.
Phosphoproteomics
♦ Includes what is offered in Complete Service with the additional step of TiO2
phosphopeptide enrichment and PTM localization or site analysis from Proteome
Discoverer/Spectronaut/Spectromine. The deliverable will be an Excel file with
phosphopeptide site analysis.
Custom Development
♦ Billed hourly and may consist of Analytical Development and optimizing digestion with specific or difficult samples.
___________
Guidelines
How Many Samples Should I submit?
Sample numbers should be determined based on power analysis or expected magnitude of protein changes group to group. Otherwise, 4 samples per group are required. Pilot studies must contain at least 3 samples per test group.
How Much Protein Do I Need to Submit?
Users should aim to have a protein concentration in the range of 0.5-6ug/uL.
Typical submission amounts are 50-200ug of total protein
A minimum of 10ug of total protein may be submitted. Any samples with less than 10ug of total protein must be discussed with the core director prior to submitting samples.
For all profiling projects, total protein concentration must be determined for each sample prior to tendering samples to the core for analysis. A detergent-compatible BCA may be used, and concentrations must be noted in the Sample Manifest File when submitting a request via iLabs in addition to specifying how samples should be grouped for analysis.
Failure to do so will result in delays and additional fees.
For Gel bands (Coomassie and Silver-stained) for protein identification will be rejected unless they are cubed (~1mm) in 1.5mL centrifuge tubes and destained.
For Immunoprecipitation, Pull-down, or Interactomic studies:
- Sample numbers should be at least n=4 or more and require at least 200ug of just protein (not beads).
- IP and pull-downs must be optimized and eluted with an appropriate mass spec-friendly buffer (e.g. 5%SDS and 50mM Triethylammonium Bicarbonate Buffer (pH 8.5) or 2× NuPAGE™ LDS Sample Buffer supplemented with 20 mM DTT and 2 mM biotin for Turbo or BioID studies).
- The sequence of the bait protein must also be included in the FASTA file.
- IP antibody control (i.e. non-specific binding control with no antibody) must be included.
Use a Coomassie gel to verify your pull down was successful (western blotting is not enough).
Failure to include any of these will result in delays and additional charges.
The Sample Manifest File must still be used when submitting a request via iLabs to specifying how samples should be grouped for analysis.
Failure to do so will result in delays and additional fees.
What or How should I Lyse/Homogenize With?
Lysis Buffer: 5% SDS in 50mM Triethylammonium Bicarbonate (TEAB) pH~8 or 5% SDS in 50mM TEAB with 4M Urea to aid to solubilizing difficult to homogenize cells or tissues. 1M TEAB stock may be purchased from Sigma Aldrich (T7408).
Cell pellets or tissues: Collect your cell pellet via centrifugation, wash at least twice in PBS, carefully remove as much PBS as possible before adding and equal volume of lysis buffer. Sonicate on ice until homogenized and not viscous. If viscous, add more SDS lysis buffer in low volume increments (e.g 20uL) to keep proteins concentrated. Tissues may be homogenized in 2x volume of SDS lysis buffer using a mill, dounce homogenizer, bead beating, or sonication taking care to avoid excessive foaming. Following lysis and homogenization, centrifuge to pellet debris or insoluble portion and determine protein concentration prior to aliquoting or freezing.
Plasma or biofluids including cell culture media: supply neat aliquots that are depleted of albumin or common proteins. Contact core director prior to submitting plasma, sera, or media for protein profiling for recommendations on sample depletion or concentration methods.
NOTE: Detergents in buffer are the major areas of concern for all users.
Compatible Detergents: 0.05%-12% SDS, 0.05%-0.5% CHAPS (sodium deoxycholate, Triethylammonium bicarbonate are also MS friendly reagents). SDS based or mild detergent buffers can be used with our SDS-Trap columns and SDS-based detergents are recommended.
Incompatible Detergents/Buffer Components: Nonidet P-40 (which can no longer be purchased; Sigma is substituting CAIgepal 630), Triton® X-100 (or any derivative), Igepal/PEG (any derivative), Brij®-35 (or any derivative), Tween®-20, OTG, CHAPSO, Type NP40/NP40 alternative.
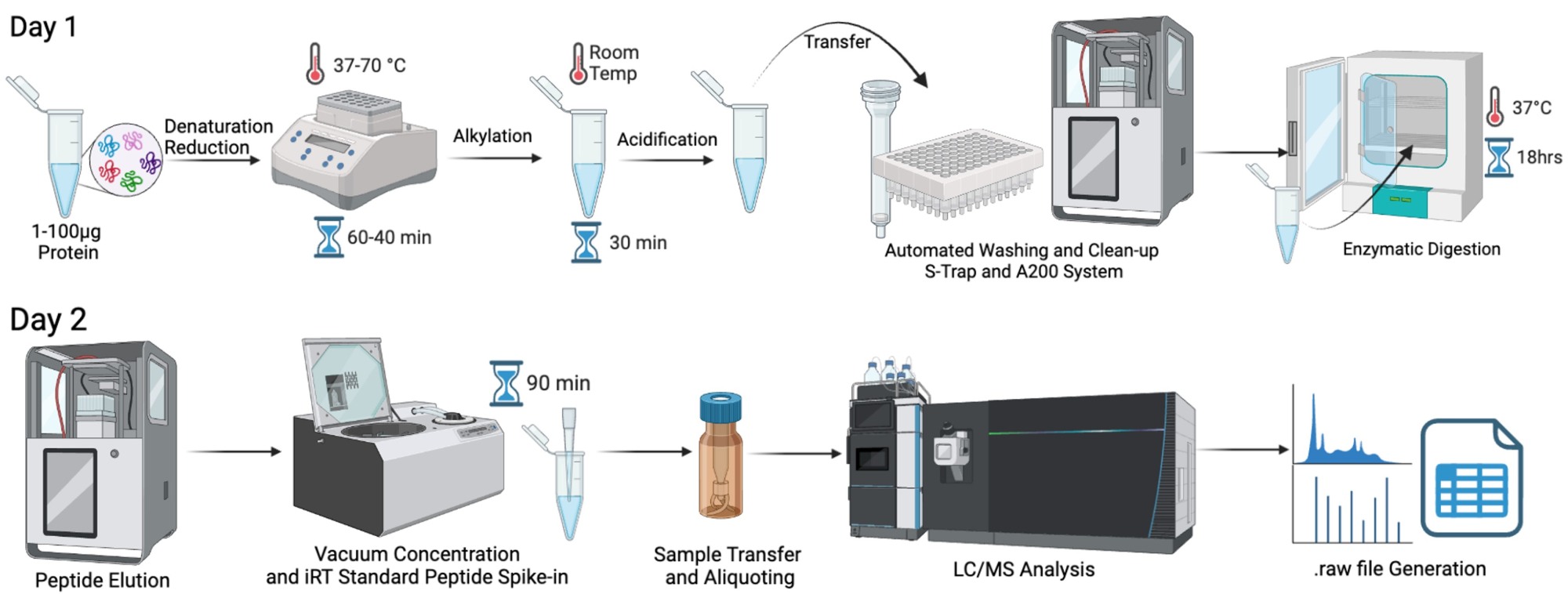
Sample Workflow
Service Requests and Reservations
To request service, please go to Brown iLab
Login with your Brown credentials and select the Proteomics Core from the drop-down menu. Then click on “request services” and select either Project Planning, Protein Profiling, or PTM Analysis to fill out an experiment design and sample intake form.
New External and Commercial customers click here
Rates
FY26 Rates
| Service | Units | Internal Academic Rates* | External Academic Rates | Commercial Rates |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ascend Basic Service | Sample | $133 | $228 | $455 |
| Ascend Complete Service - Protein Profiling | Sample | $192 | $329 | $658 |
| Ascend Complete Service - CoIP Interactomics | Sample | $222 | $380 | $759 |
| Ascend Phosphoproteomic Services | Sample | $233 | $398 | $795 |
| Ascend Self Use | Sample | $30 | $51 | $103 |
| Custom Service Development | Hour | $84 | $144 | $288 |
*Rates for Brown and Rhode Island Academic Institutions and Hospital Affiliates
Rates Effective 11/5/2025
Contact/Location
Facility Director
Location
Proteomics Core Facility
Brown University
Laboratories of Molecular Medicine
70 Ship Street, Room 410
Providence, RI, 02903
Directions
Laboratories for Molecular Medicine MapQuest Directions to the Laboratories for Molecular Medicine | Campus Map: LMM Building: Jewelry District- Downtown Providence | Related Links: |
Resources for Grants
Acknowledgment
This facility was supported in part by grants from the National Institutes of Health (NIH), Brown University's Division of Biology and Medicine and Provost's office.
We request that users of our facility please use this statement with the instrument used for their project(s) when acknowledging work performed in the facility:
"This research is based in part upon work conducted using the Proteomics Core Facility, which was supported in part by the National Institutes of Health Grant No. 1S10RR027027 (QExactive, Orbitrap XL-ETD), 1S10OD036295 (Ascend Tribrid, FAIMS, Vanquish Neo), and the Division of Biology and Medicine, Brown University."
